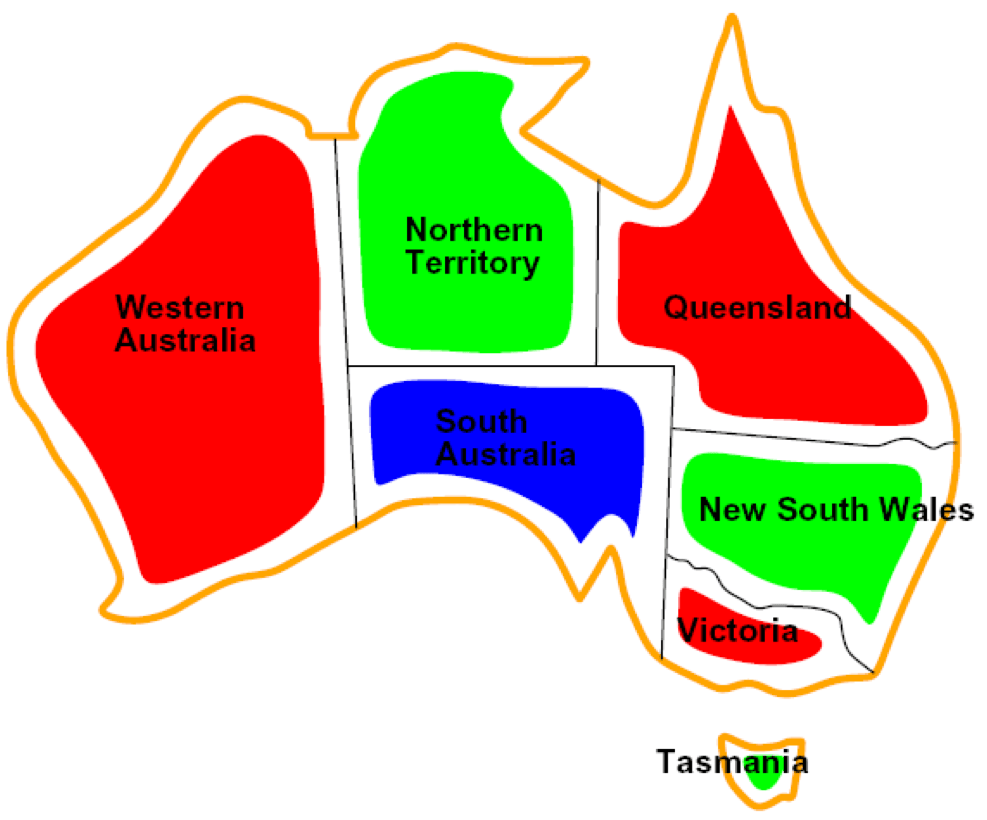
Graph Coloring Constraint Satisfaction Problem - In this blog post, we will see how to formulate csp problems using three basic components: Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree. Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. Add forward checking to the. The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring. Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values v1,., vn to each of the n nodes • the values are taken in { r,g,b}.
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) Cryptarithmetic, Graph Coloring, 4 Queen, Sudoku PPT
Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node. We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and.
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) Cryptarithmetic, Graph Coloring, 4 Queen, Sudoku PPT
In this blog post, we will see how to formulate csp problems using three basic components: We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node. Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly.
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) Cryptarithmetic, Graph Coloring, 4 Queen, Sudoku PPT
Add forward checking to the. Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring. Add variable and value ordering to the implementation.
PPT Constraint Satisfaction Problems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID584040
Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values v1,., vn to each of the n nodes • the values are taken in { r,g,b}. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree. We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. The goal.
Mapcoloring as constraint graph. One possible solution to the CSP is... Download Scientific
Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring. Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: Add forward checking to the. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree.
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Map coloring and other examples of CSP YouTube
Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is.
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) Cryptarithmetic, Graph Coloring, 4 Queen, Sudoku PPT
Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). Add variable and value ordering to the implementation. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree. In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables,.
GitHub rohitsingh186/graphcoloringconstraintsatisfactionproblem `Graph Coloring Problem
In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node. We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. In this blog post, we will see how to formulate csp problems using three basic components: Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values.
Constraint satisfaction problems ppt download
Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring. Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values v1,., vn to.
Constraint Satisfaction I
Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). Add forward checking to the. Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. Add variable and value ordering to the implementation. The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring.
Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: The goal is to assign colors to each region so that no neighboring. In this blog post, we will see how to formulate csp problems using three basic components: Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values v1,., vn to each of the n nodes • the values are taken in { r,g,b}. Add forward checking to the. Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp). We use the map coloring problem to demonstrate the csp. Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. Add variable and value ordering to the implementation. In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node. The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree.
The Goal Is To Assign Colors To Each Region So That No Neighboring.
The tree_csp_solver function (figure 6.11 in the book) can be used to solve problems whose constraint graph is a tree. Graph coloring • consider n nodes in a graph • assign values v1,., vn to each of the n nodes • the values are taken in { r,g,b}. Add variable and value ordering to the implementation. In this problem, the color of nodes in a graph (map) are the variables, the set of available colors for each node.
We Use The Map Coloring Problem To Demonstrate The Csp.
Implement the following graph coloring algorithms: In this blog post, we will see how to formulate csp problems using three basic components: Map coloring is a classic problem in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the realm of graph theory and constraint. Coloring this map can be viewed as a constraint satisfaction problem (csp).